- Home
- Continuous Improvement Certification Online
- Agile Manufacturing
Agile Manufacturing
What is Agile Manufacturing?

Agile manufacturing is a business concept that integrates organizations, people and technology into a meaningful unit by deploying advanced information technologies and flexible organization structures to support highly skilled, knowledgeable and motivated people.
An agile manufacturing strategy would use processes, tools and training, which enables it to respond to these needs and changes rapidly without jeopardizing the cost and quality of the product.
The focus of agile manufacturing lays on the response time and the aim is to react to customer needs quickly. Therefore, agility and speed become the competitive advantages of agile manufacturing.
Agile Manufacturing represents a very exciting approach to developing a competitive advantage in today's fast-moving market. An extremely strong focus is placed on quick customer response - speed of change and agility a key competitive advantage. An agile company is in a better position to take advantage of short windows of opportunity and rapid changes in customer demand.
Agile manufacturing is a method of incremental development of a product in a feedback process aimed at continuous improvement, it was created in response to lean or traditional manufacturing. It differentiates itself by focusing on meeting customer requirements without sacrificing quality or additional costs. The idea is based on the concept of the virtual company and you want to build flexible, often short-term relationships with suppliers when market opportunities arise.
The key elements of Agile Manufacturing

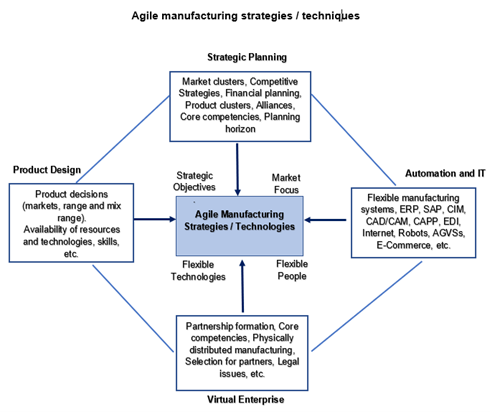
The model of agile manufacturing is built on four core elements. These include Modular Product Design, Information Technology, Corporate Partners, and Knowledge Culture.
Modular Product Design:
Agile manufacturing tends to create products, which allow modification and variation quickly. This is best achieved by the Modular Product Design approach, which means products are designed in a modular fashion. Modular products are typically built from a number of different pieces, allowing fast and easy variation.
For example, instead of
creating the product from a single piece of material, the manufacturer would
create smaller pieces that fit together to create the product. If you’d want to
change a specific aspect of the product, you wouldn’t need to change the whole
process.
Information Technology:
Agile manufacturing also involves the use of information technology, especially in order to improve internal and external communication. Proper implementation of information technology allows employees to make decisions quicker in terms of product design. Furthermore, it allows a rapid response time to customer queries, as information is disseminated quickly across the different platforms.
Corporate Partners:
On the contrary to the traditional model of manufacturing, the agile manufacturing model aims to leverage relationships with other companies. Short-term partnerships and co-operative projects are encouraged, as they can help the company to enter and adjust to new or changing markets quicker.
The difference between lean manufacturing and agile manufacturing

When an organization is considering ways to organize its manufacturing process, they can come across another manufacturing concept called lean manufacturing. While both lean and agile manufacturing can help companies lower costs, improve customer service and boost responsiveness, there are certain differences in these methodologies.
Lean manufacturing is focused on minimizing the costs of manufacturing. The focus is therefore on demand-based manufacturing, which aims at eliminating investments in inventory. Lean manufacturing involves improving the effective use of utilities, facilities and materials. The process is driven by the mind-set that it can be constantly improved to make manufacturing more cost efficient. Therefore, lean manufacturing emphasizes improvement and the measurement of performance.
You could view both models
through the analogy of a person. One could be a thin person or one could be a
fit person. Thin and fit is not the same, but a person can also be thin and
fit. Similarly, an organization can be a lean or an agile manufacturer, or the
company could become both. However, an agile manufacturing plan doesn’t
automatically mean it’s also lean.
In fact, lean manufacturing is often considered the precursor of agile manufacturing. This is because lean practices can enable agile manufacturing practices.
The similarities of these models include:
- Support of revenue creation and sustainability
- Improved competitiveness
Agile! Become a high-responsive entrepreneur, director, manager, operative, etc. You are key to success, your training is a high value asset.