- Home
- Continuous Improvement Certification Online
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Flexible Manufacturing Systems
What is a flexible manufacturing system (FMS)?
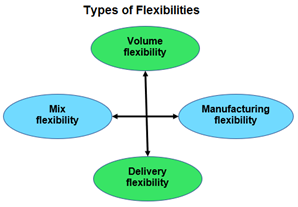
When spoken in the context of manufacturing, flexibility is a general term used to describe the ability of a manufacturing system to adjust better handle nuances such as mixed parts, assembly variations, process sequence variations, changes in production volume, changes in design, etc. and other changes.
FMS consists of a group of processing workstations interconnected by means of an automated material handling and storage system and controlled by integrated computer control system.
In essence, an FMS is a method used to manufacture and produce goods that can adapt to change. Whether these changes involve adding new product types, modifying existing product types, etc., an FMS can handle these and more.
Its use provides manufacturing companies with a great competitive advantage over their counterparts that do not use such flexible systems.
FMS ensures quality product at lowest cost while maintaining small lead-time. So, firms adopt FMS as a means of meeting burgeoning requirements of customized production. Main purpose of FMS is to achieve efficiency of well-balanced transfer line while retaining the flexibility of the job shop. A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) has four or more processing workstations connected mechanically by a common part handling system and electronically by a distributed computer system. It covers a wide spectrum of manufacturing activities such as machining, sheet metal working, welding, fabricating, scheduling and assembly, among others.
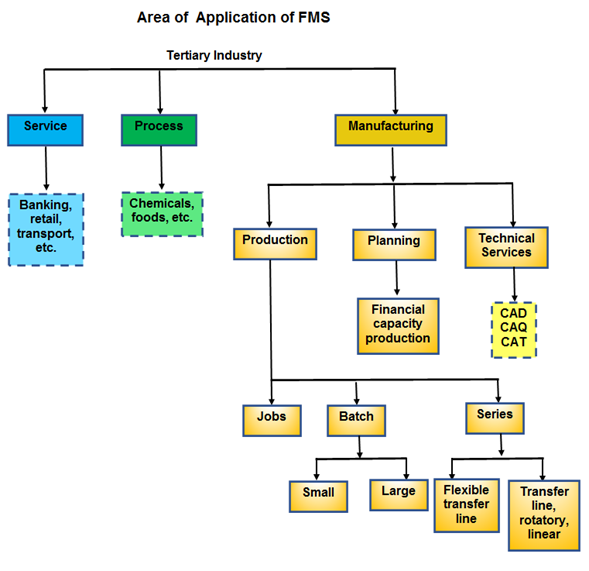
The basic components of FMS are:
- Workstations.
- Automated Material Handling and Storage system.
- Computer Control System.
The different types of FMS are:
- Sequential FMS
- Random FMS
- Dedicated FMS
- Engineered FMS
- Modular FMS
In relation to the types of FMS layouts these are:
- Progressive or Line Type
- Loop Type
- Ladder Type
- Open field type
- Robot centered type
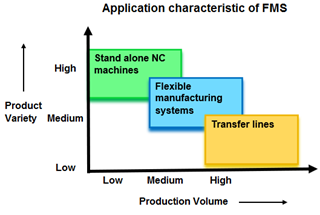
Why implement FMS?
8 station system, linear transfer, FMS lateral view:

Cell with 8 robots, 3 machining centers, several automated warehouses, loading stations.
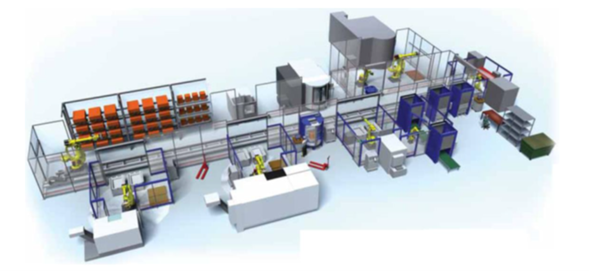
The benefits that can be achieved by successfully implementing a flexible in the manufacturing system in the correct environment are quite substantial. Some of these advantages are more difficult to evaluate than others however, a list of the advantages which might typically be expected to result:
- Improved capital / equipment utilization.
- Reduced work in progress and set-up.
- Substantially reduced throughput times/lead times.
- Reduced inventory and smaller batches.
- Reduced manpower.
- Ability to accommodate design changes readily.
- Consistent quality
- Increased management control over the entire manufacturing process.
- Reduced risk as a result of specific product failure.
- Concise management control.
- Improved market image/credibility.
- Reduced floor space requirements.
- Substantial economic benefits.

The FMS imply a change of philosophy of production. It is necessary to carry out a series of preparatory tasks prior to the implementation of the FMS.
Just in time:
FMS help implement the “Just in Time” philosophy, which means manufacturing only what is strictly necessary, when necessary, and only in essential quantities.
The objective is to reduce stocks to the minimum necessary.
Coding:
It is necessary to classify and code each of the pieces in the family so that the correct program can be used on the correct machine. This requires organizing all the parts into families, coding each part of the family to assign a series of manufacturing orders (CNC programs, specific machines, etc.).
There are countless companies that are incorporating Flexible Manufacturing Systems into their processes, due to the advantages that this represents, however it is also decisive to assess the investment that this represents, within the scope of the project to be developed, among other aspects to consider.
Let us support you in delving deeper into this methodology than in complement with Lean and Six Sigma, you will achieve high impact elements for the benefit of your projects, your organization and in achieving maximum performance.
InArtifexYou has a team of specialists who can train you and help you bring your project to fruition.
Add up to our community!